Thyroid Cancer Genomics
(BRAF, HRAS, KRAS, NRAS, RET, TERT Promoter)
NTRK1 rearrangements have been shown to be involved in thyroid carcinogenesis. Several studies Show that NTRK1 rearrangements may be associated with a worse clinical course when compared with NTRK1 rearrangement-negative Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas.The treatment of patients with NTRK fusion-positive cancers with a NTRK inhibitor, such as the FDA approved drugs Larotrectinib or Entrectinib, is associated with high response rates regardless of NTRK gene, fusion partner, and tumor type. Hence, detection of NTRK1 rearrange-ments by in situ Hybridization. may be of prognostic and therapeutic significance.
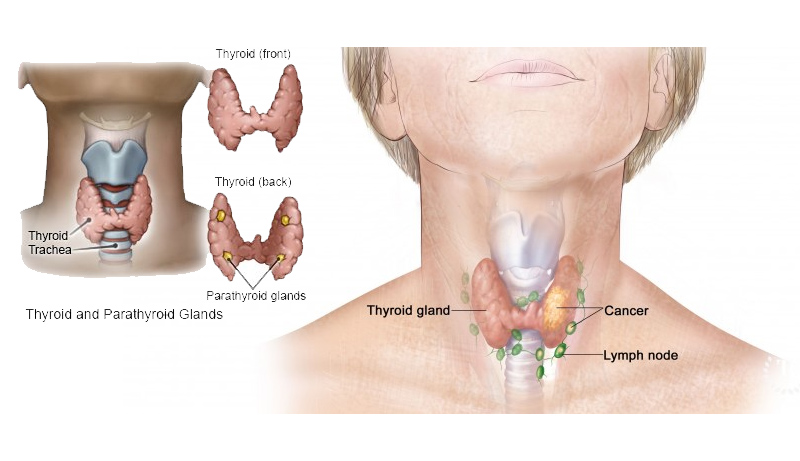
THYROID CARCINOMA is a rare malignancy but its occurrence is still increasing worldwide
- Females are affected 4 times more often than males, and ionizing radiation exposure is the only well recognized risk
- No pre surgical serum markers are known for DTC, while high levels of serum Ct are diagnostic of MTC
- The most common oncogenic alterations are BRAFV600E and RET/PTC rearrangements in DTC, and RET point mutations in MTC
- The prognostic factors for both recurrence and survival are advanced age and/or an advanced stage at diagnosis
- Thyroidectomy is the initial treatment of thyroid Lymphadenectomy should be performed only if there is evidence of metastatic lesions at neck US
- 131-I treatment is performed in DTC cases with an intermediate or high risk of recurrence, while it cannot be used in MTC or in ATC
- DTC and MTC patients can be followed by measuring serum Tg and Ct, respecti Neck US is fundamental in their follow-up
- New targeted therapies have recently been approved for the treatment of advanced and progressive DTC and MTC
- ATC is still orphan of successful therapies, and are still lethalTC is a rare malignancy but its occurrence is still increasing world-wide